Hematology-Oncology
What Is the Specialty of Hematology-Oncology?
Well, actually, it’s a sub-specialty, because to become a Hematologist-Oncologist, a doctor must first complete residency training in the specialty of Internal Medicine and then complete fellowship training in the sub-specialty of Hematology-Oncology. Hematology pertains to the study, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases related to the blood and blood forming tissues. The term is derived from the Greek word, haima, meaning blood. Oncology pertains to the study, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of neoplasms (tumors, cancer). Again, we get the term from Greek, this time from the word, onkos, meaning bulk or tumor. So why are these two disciplines linked together into one sub-specialty?
How Are Hematology and Oncology Related?
There are two reasons why it makes sense for the same sub-specialist to practice in these two disciplines. First, many of the malignancies that an oncologist treats originate in the blood forming organs, for example leukemia, lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Second, the treatment for many types of cancer have a deleterious effect on the various types of blood cells as an unwanted side effect. Fine tuning the treatment of malignancies, while at the same time managing the complications of that treatment is an art in itself and requires extensive knowledge of the blood cell system. So, in addition to being an expert in treating blood disorders which develop spontaneously, the Hematologist-Oncologist is ideally suited to treat malignancies and the blood disorders resulting as a complication of that treatment.
A Few More Interesting Points
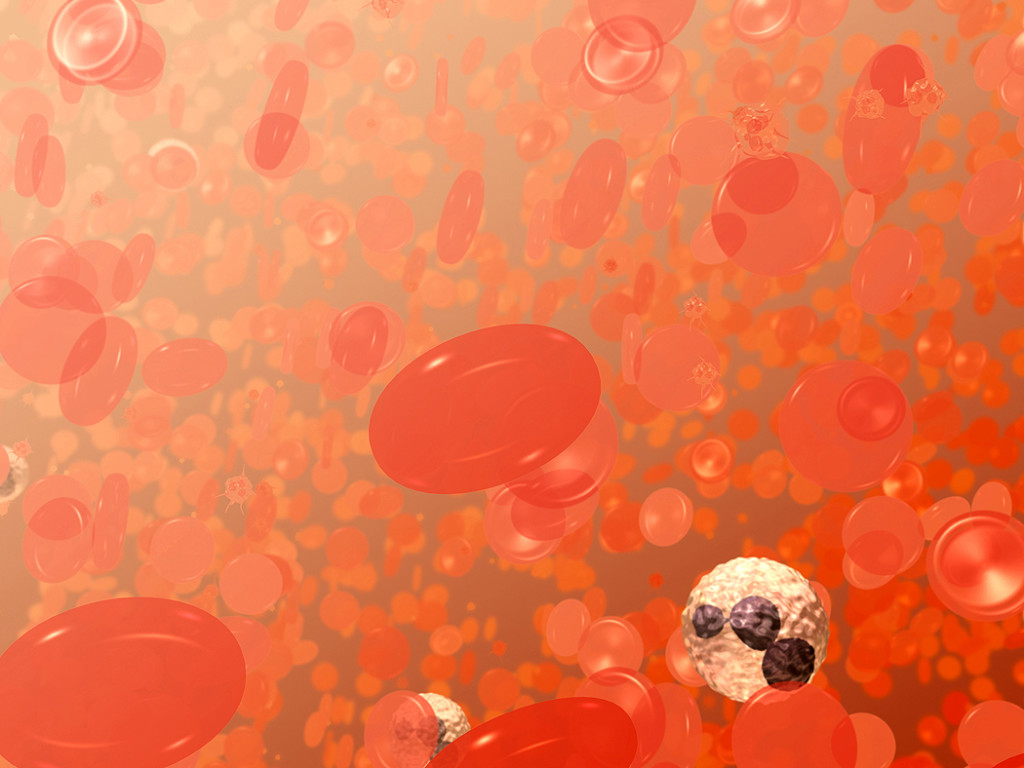
The CBC or Complete Blood Count is a laboratory test performed on blood that is withdrawn from a vein. It is used to measure the levels of different types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. The red blood cells have a limited life span of about 120 days and contain a protein called hemoglobin which carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. The white blood cells are part of the immune system and help fight infections. The main function of platelets is to help stop bleeding. Each of these blood elements is formed in the bone marrow, where they grow rapidly and have a fast turnover time. Many chemotherapy drugs are effective against malignancies because they take advantage of the rapid turnover times of the cancer cells they are targeting. Unfortunately, good cells, like the blood elements, are also susceptible to the toxic effects of chemotherapy drugs because of their rapid turnover times.
Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells and Platelets
Hematology-Oncology Read More »